The Center for Improving Value in Health Care (CIVHC) recently released its sixth update to the Telehealth Services Utilization Analysis, which now includes data from 2019 through 2023. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, reshaping health care delivery in Colorado. Using claims data from the Colorado All Payer Claims Database (CO APCD), the Telehealth Services Analysis provides critical insights into this transformation. The latest data shows that nearly five years after the onset of COVID-19, telehealth remains a vital source of care, especially for Coloradans accessing mental health services.
The analysis shows that while overall telehealth usage has decreased from its initial pandemic peak, demand for services with behavioral health and primary care providers remain much higher than pre-pandemic levels. In 2020, telehealth services with primary care providers peaked at 69 services per 1,000 people per month but has stabilized to approximately 15 services per 1,000 people. Telehealth services with behavioral health providers have consistently dominated telehealth visits, averaging around 35 services per 1,000 people monthly since 2020.
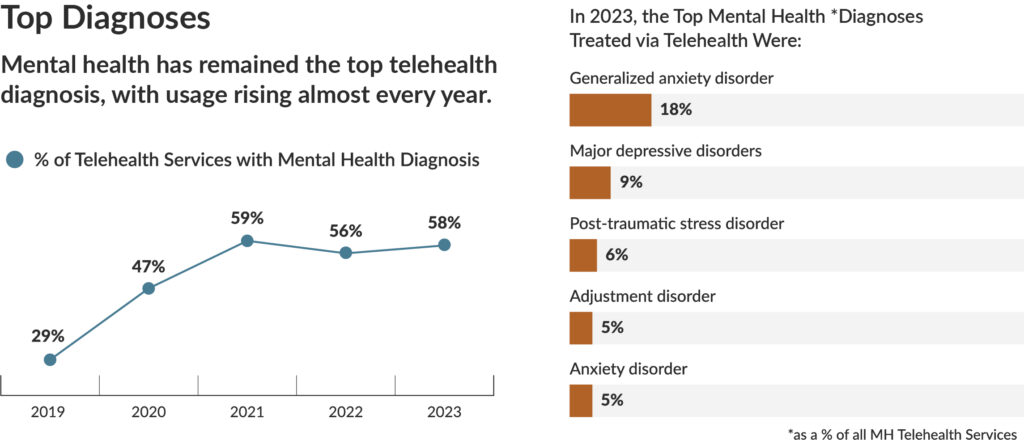
Across all provider types, telehealth visits for mental health related reasons continue to trend upward representing 47% of all visits in 2020 and 58% of all visits in 2023. Telehealth is crucial for providing access to mental health care, and helps reduce barriers like provider shortages, travel time, and stigma. In 2023, general anxiety was the most common telehealth mental health diagnosis, making up 18% of all visits, followed by depression (9%), post-traumatic stress (6%), adjustment (5%), and anxiety (5%).
This latest release also explored geographic differences between telehealth use in rural and urban areas. In rural communities, Medicaid-insured patients received the most telehealth visits (40%), and in urban areas commercially insured patients had the most visits (42%). Approximately 86% of people in Colorado live in urban counties, and these residents made up 92% of all of the telehealth visits statewide. Despite some geographic differences, mental health conditions emerged as the leading diagnosis for both rural (83%) and urban (86%) residents, followed by endocrine and nutritional conditions.
Additional Resources:
- Telehealth Services Analysis Infographic
- Telehealth Services Analysis Methodology
- Access the Data File
For more information or additional questions, contact us at info@civhc.org .